
How to Use Lidar Drone for Mapping and Surveying?
In recent years, the use of lidar drone technology has transformed mapping and surveying processes. Lidar drones offer precise data collection capabilities, even in complex terrains. They capture high-resolution images and detailed topographical information, making them invaluable tools for professionals in various industries.
Many surveyors have begun to realize the advantages of lidar drone applications. However, mastering this technology can be challenging. Users must understand how to set up equipment properly and choose the right settings for their specific needs. This learning curve can lead to frustration and potential setbacks in projects.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of using lidar drones for mapping and surveying far outweigh the difficulties. Accurate results can save time and reduce errors in planning. Embracing this technology can lead to improved workflows, but users should remain open to continual learning and adaptation. With practice, lidar drones can redefine how we perceive and interact with geographical data.

Understanding Lidar Technology and Its Applications in Mapping
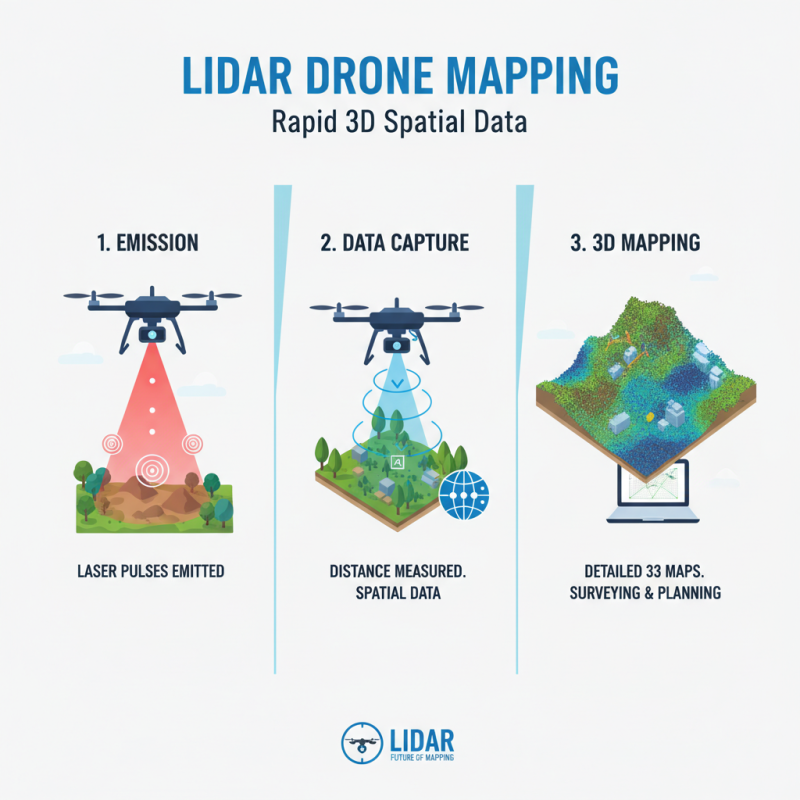
Lidar technology operates on the principle of emitting laser pulses to measure distances. It gathers spatial data quickly. Drones equipped with Lidar can cover large areas in a fraction of the time required by traditional methods. The data collected results in detailed 3D maps, making it ideal for surveying and mapping applications.
Mapping with Lidar has various real-world uses. It helps in topographic surveys for construction or land-use planning. The technology captures fine details, like vegetation and terrain changes. However, interpreting this data can be challenging. Operators need training to analyze results effectively. Mistakes in data processing can lead to inaccurate conclusions.
Despite its advantages, Lidar isn't flawless. Environmental factors, like heavy rain or fog, can disrupt data collection. Users should be aware of the limitations and plan accordingly. Testing and calibrating equipment before each flight is crucial. Continuous refinement of techniques ensures better results over time.
Choosing the Right Lidar Drone for Surveying Tasks
When selecting a lidar drone for surveying tasks, consider the project’s specific needs. Think about the area size and the type of terrain. A lightweight drone may struggle in heavy vegetation or rough landscapes. Conversely, a more robust model can handle these conditions but may be more expensive.
Battery life matters too. Short battery life can disrupt your workflow. Aim for a drone that offers ample flight time, especially for larger areas. Don’t underestimate the importance of ease of use. A complicated interface can hinder efficient mapping.
Finally, pay attention to data quality. High-resolution lidar data is crucial for accurate results. Review user feedback to gauge performance in various conditions. Every project has unique challenges, so remain flexible in your choice. Keep preferences and priorities in mind as you navigate this process.
Mapping and Surveying with Lidar Drones
Preparing Your Site for Lidar Drone Mapping and Surveying
Preparing a site for lidar drone mapping and surveying involves careful planning and execution. Start by assessing the area you wish to scan. Clear vegetation and obstacles to ensure a clean line of sight. According to industry reports, 80% of lidar survey failures stem from poor site preparation. This statistic highlights the importance of a well-prepared site.
Consider the weather conditions as well. Lidar systems do not perform well in heavy rain or fog. These elements can distort the data and impact the quality of the survey. Ideal conditions include clear skies and mild winds. It's essential to monitor the forecast closely leading up to the survey day.
Tip: Always conduct a test flight before your main survey. This can help identify any unforeseen issues. Observe the drone's performance and tweak settings if necessary. Additionally, engage with local stakeholders. Their input can provide insights that enhance data quality. Any oversight in communication may lead to significant data gaps. Proper site preparation is not just a formality; it is vital for successful lidar mapping.
How to Use Lidar Drone for Mapping and Surveying
| Dimension | Details |
|---|---|
| Site Preparation | Clear vegetation and obstacles to ensure an unobstructed flight path. |
| Equipment Required | Lidar Drone, Ground Control Points (GCPs), GPS Equipment. |
| Flight Planning | Use mapping software to define flight paths, altitudes, and overlap. |
| Data Collection | Execute the flight plan, capturing data at specified intervals. |
| Post-Processing | Analyze and refine data using specialized software to produce maps. |
| Common Applications | Topographic mapping, construction site surveys, environmental monitoring. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Ensure adherence to local drone regulations and privacy laws. |
Data Processing Techniques for Lidar Mapping Outputs
Lidar technology has revolutionized mapping and surveying. Its ability to capture high-resolution data makes it invaluable. However, processing this data efficiently remains a challenge. The raw outputs from Lidar drones include vast amounts of point cloud data, which requires careful handling.
Data processing techniques directly impact the quality of the final outputs. Using algorithms for noise reduction can help clarify ground features. For instance, noise can obscure critical details, leading to inaccuracies. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) reports that effective noise filtering can improve data precision by up to 30%. This emphasizes the importance of software choices in the data processing stage.
Another technique involves classifying point clouds into categories like ground, vegetation, and structures. This classification aids in creating accurate digital terrain models. Industry reports show that using machine learning for classification can enhance speed and precision significantly. However, improper training data can lead to misclassifications. This highlights a common issue in Lidar processing—striking a balance between automation and accuracy remains challenging.
Best Practices for Analyzing and Interpreting Lidar Data
Lidar technology has transformed mapping and surveying. When analyzing Lidar data, accuracy is crucial. Start by carefully selecting the data resolution based on your project requirements. High-resolution data may offer more details but can be harder to process. Ensure your software is up-to-date for optimal performance.
Tips: Use filters to remove noise. This will improve the quality of your analysis. Remember to validate your findings with ground truth data. A mismatch could lead to significant errors in the project. Embrace the challenge of interpreting complex datasets.
Interpreting Lidar data requires practice. Familiarize yourself with the software tools, as they can vary. Experiment with different visualization techniques to find what best reveals the data. Sometimes the results can be confusing at first. Don’t hesitate to revisit initial assumptions, especially if results seem off.
Tips: Collaborate with peers. They can offer fresh perspectives. Challenge yourself to spot patterns that may not be immediately obvious. Analysis is not just about numbers; it’s about understanding the landscape.
Related Posts
-
Top Uses of Infrared Drones: Why They're Essential for Modern Aerial Surveys
-

What is a 4K Drone and How to Choose the Best One for Your Needs
-

What is a DIY Drone and How to Build One Step by Step Guide
-

How to Choose the Best UAV Drone for Your Needs and Budget
-

Top Nano Drones to Watch in 2025 for Aerial Photography and Fun
-

How to Choose the Best Professional Drone for Your Needs




